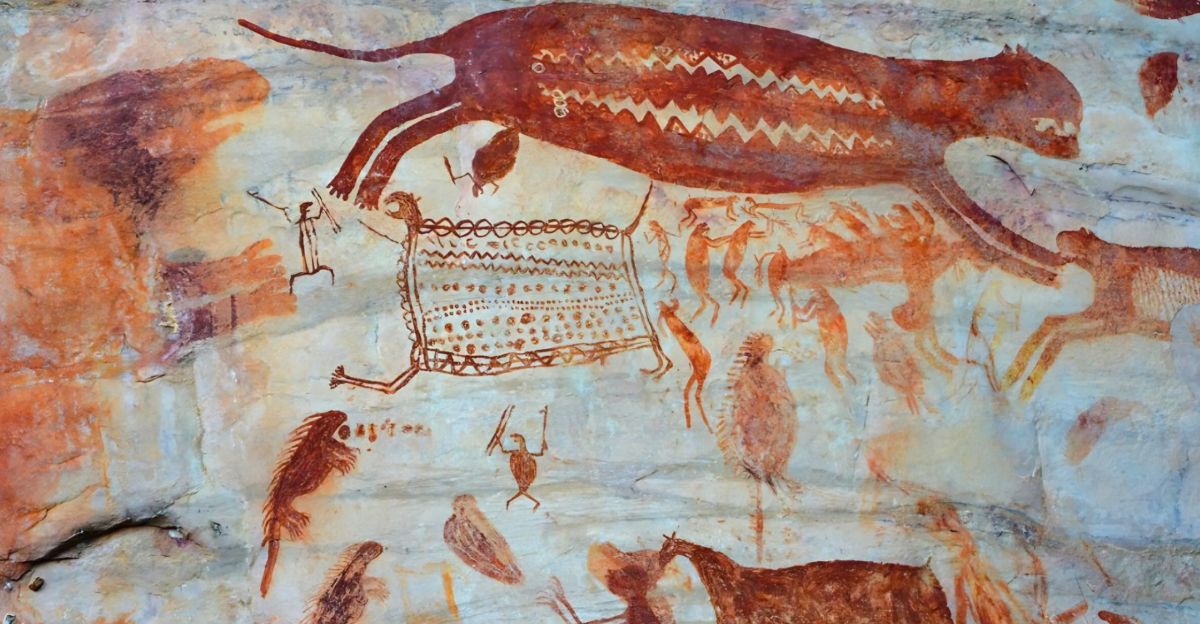
Some of the earliest evidence of human life in the western edge of the Amazon has been discovered in a range of rock shelters in Colombia. Some 12,500 years ago, these ochre paintings offer a rare glimpse into the lives of prehistoric people.
The artwork, painted on cliff faces, includes thousands of images depicting humans, animals and geometric patterns, and represent a rich cultural and ecological history of the region.
A Treasure Trove of Prehistoric Art

The Serranía de la Lindosa site is renowned for its vast collection of rock art created using red and yellow ochre pigments.
These natural materials have preserved the paintings for millenia, showcasing the artistic skill and knowledge of ancient Amazonian communities.
The durabilityof the pigments allows modern researchers to study the cultural expressions and environmental interactions of these early peoples.
Depictions of Extinct Megafauna Reveal Ice Age Coexistence

Among the most striking features of the rock art are depictions of now-extinct megafauna. These include giant sloths, mastodons and ancient relatives of elephants that roamed South America during the Ice Age.
The inclusion of these animals in the artwork reveals that humans coexisted with these large creatures, offering unique perspectives on prehistoric environments and relationships between humans and animals.
Human Figures Depict Social and Cultural Practices
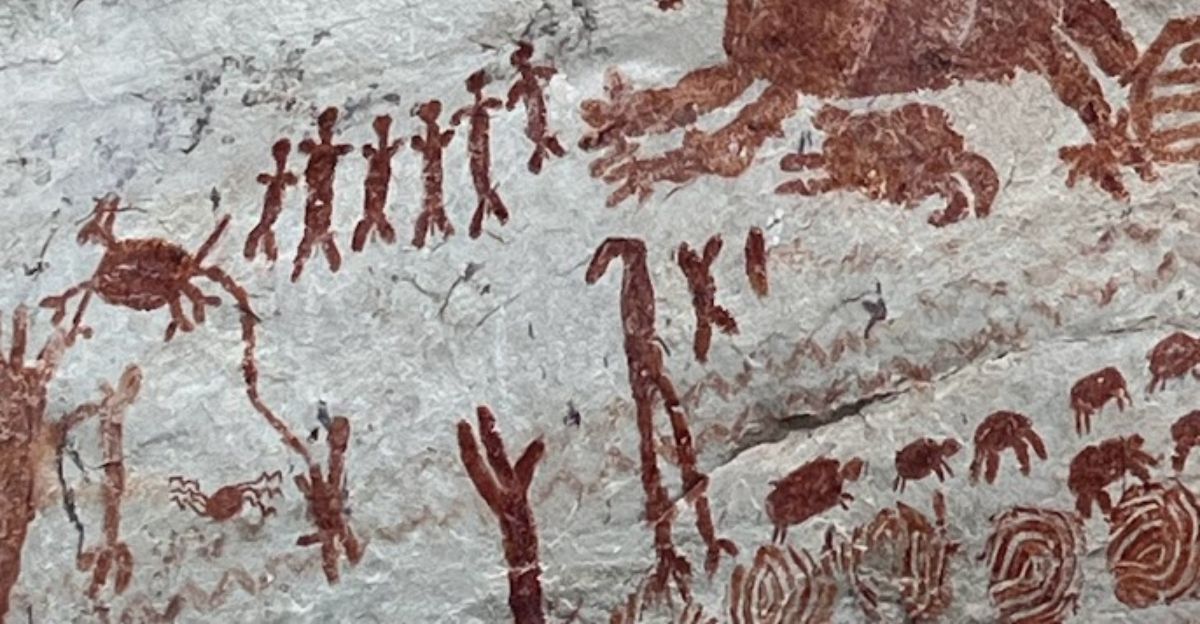

The human figures in the paintings are shown engaged in various activities such as hunting, dancing and interacting with the animals. This reflects the social and cultural practices of the time, emphasizing trhe importance of community and the complex relationship between humans and their environment.
Some images even depict humans and animals morphing into one another, suggesting rich mythological beliefs abd shamanistic practices among these ancient peoples.
Symbolism and Shamanistic Beliefs in Rock Art

The art is filled with symbolism and many of the paintings are representations of these interconnections of life forms. The transformational scenes between humans and animals suggest spiritual systems in which ritual specialists negotiating with supernatural forces.
This complexity suggests that early Amazonian societies had sophisticated cultural frameworks beyond mere survival.
Biodiversity Reflected in Ancient Amazonian Paintings
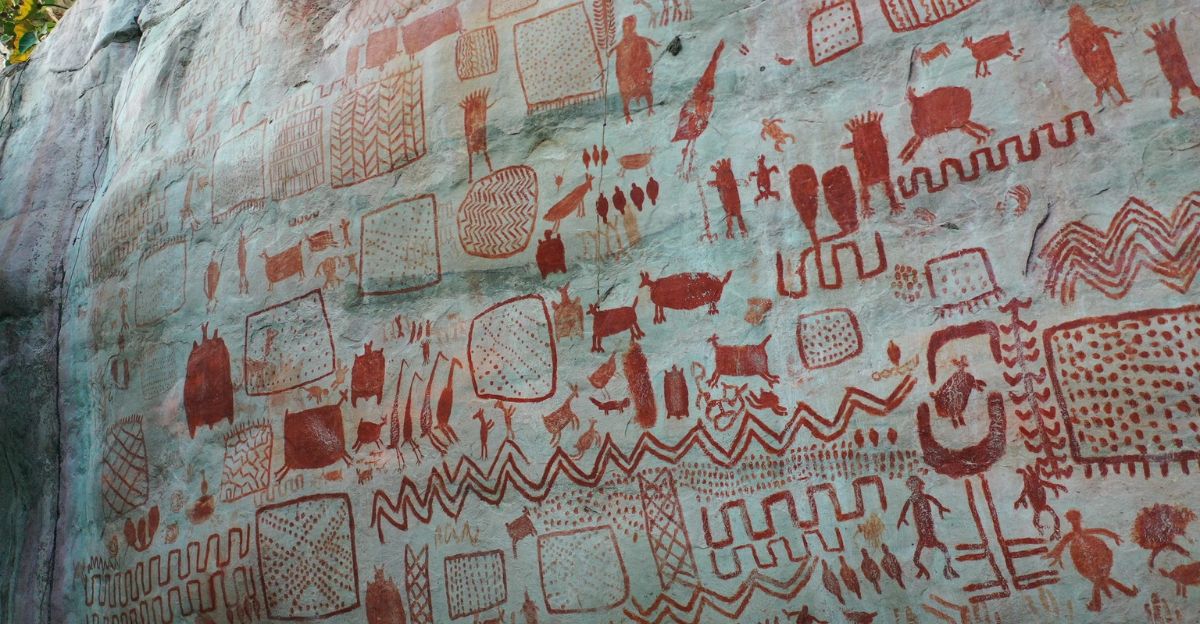

A diversity of animals depicted in the rock art reflects the rich biodiversity of the ancient Amazonian rainforest. There are images not only of megafauna but of deer, birds, lizards, turtles, tapirs and other native species.
Such diversity reflects the rich natural resources available to early humans and their deep ecological knowledge of the region.
Archaeological Significance for Human Migration Studies

The archaeological context is also important for the interpretation of rock art, because it helps to shed light on the migration and settlement patterns in South America.
The depictions of extinct animals help establish timelines for human habitation and interactions with megafauna, contributing to broader narrative about prehistoric life and environment changes in the Amazon basin.
Challenges and Innovation in Rock Art Preservation

Preservation of these ancient paintings is a difficult task as the paintings are subjected to weathering, growth of vegetation and environmental elements.
Conservation efforts have involved sophisticated technologies such as drone photogrammetry, which documents the site in elaborate detail for future study. These actions are necessary to preserve the historic and cultural value of the rock art.
Cultural Importance for Contemporary Indigenous Communities

For contemporary indigenous communities, the rock art holds profound cultural and ancestral significance. It serves as a tangible link to their heritage and provides insights into the beliefs and practices of their forefathers.
Respecting this connection is essential for preserving the integrity of the site and the honoring its ongoing cultural relevance.
Comparitive Studies and Further Research

Comparitive studies with other Amazonian and South American rock art sites reveal widespread artistic expression among early human populations.
These analyses help researchers understand regional variations, cultural exxhanges and adaptations, enriching our knowledge of prehistoric societies and their environments.
Future interdisciplinary research promises to uncover even more about the social structures, economies, and spiritual lives of these ancient Amazonian peoples.