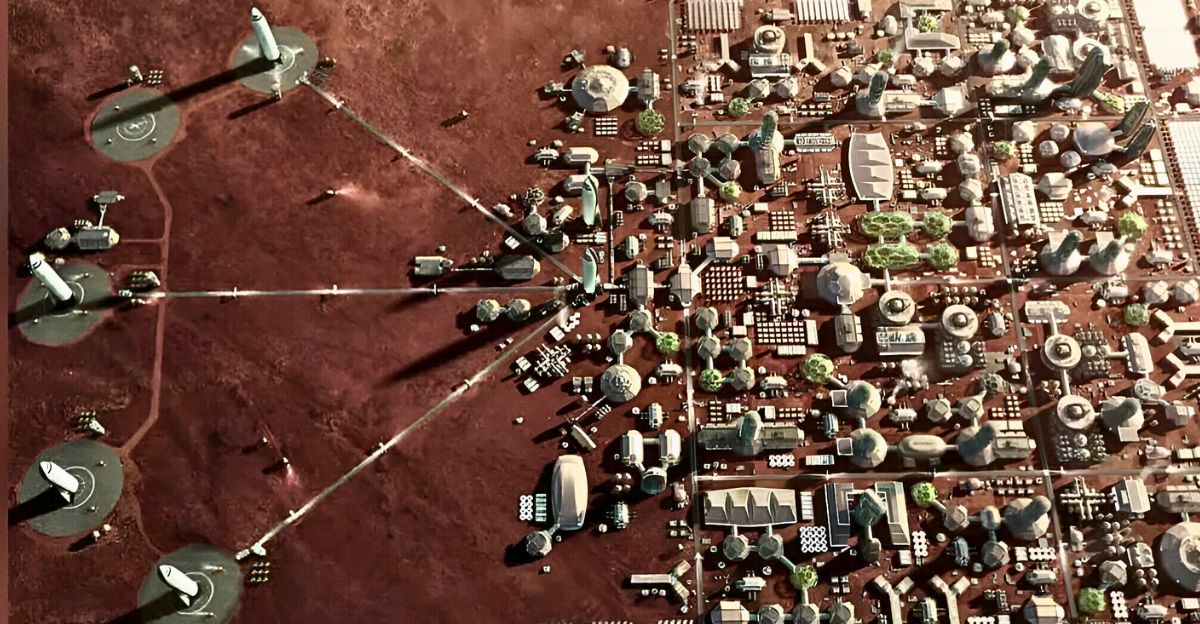
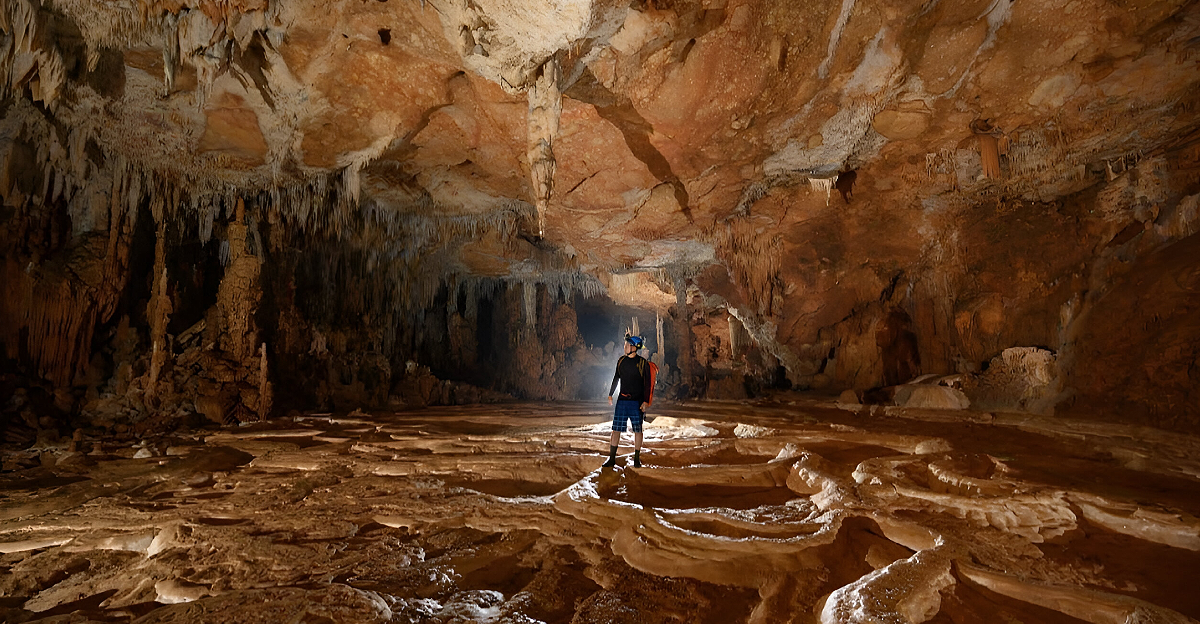
The need for NASA and SpaceX to build an underground Martian civilization is a strategic necessity, not just science fiction bluster. Because of the deadly cosmic radiation, dust storms, and extreme temperature fluctuations that plague Mars’ surface, traditional above-ground living is not feasible for long-term human survival. The goal of the race is to ensure that humanity will continue to exist as a multi-planetary species before the window of opportunity is closed by Earth’s geopolitical, ecological, or existential crises. It is not just about beating the clock.
Because Mars is humanity’s insurance policy, the stakes are existential. Furthermore, by avoiding the need to transport bulky shielding materials from Earth, the underground method takes advantage of Mars’ geological features to cut down on construction time and costs. This approach fits with the larger goal of sustainable colonization, which emphasizes resilience and self-sufficiency.
Patterns from History

The Cosmic Warto of Cold War History demonstrates that technological advancements are driven by existential threats. The space race that resulted in Apollo’s lunar victories was sparked by the Cold War’s nuclear anxieties. The habitability of Earth is currently threatened by resource depletion, climate change, and geopolitical instability. In response, NASA and Elon Musk’s SpaceX are engaged in a new race—not against one another, but against time.
The way that competition and cooperation have coexisted in space exploration to advance humanity is also revealed by this historical perspective. As evidenced by NASA’s collaborations with international organizations and private businesses like SpaceX, the urgency of the Cold War not only spurred innovation but also taught the value of international cooperation.
Martian Subterranean Science

Living With radiation doses up to 250 times higher than on Earth, Mars’s thin atmosphere provides very little protection from radiation. Lava tubes are large, stable tunnels created by ancient volcanic activity that can be used in underground habitats. In order to protect life from radiation, extreme temperatures, and micrometeorites, NASA has identified over 1,000 possible cave entrances, some of which are visible through enigmatic holes that are 328 feet wide.
Using drones and radar, scientists are already mapping these underground networks in an effort to determine which locations would be best for human habitation. This scientific foundation is essential for creating habitats that blend in perfectly with Mars’ natural surroundings, reducing ecological disturbance while optimizing human comfort and safety.
Robotic Solutions and Engineering Difficulties
The development of AI-driven construction techniques, autonomous rovers, and robotic swarms will enable the excavation, processing, and assembly of habitats prior to human arrival. Previously considered science fiction, these technologies are currently undergoing testing on Earth and will serve as the foundation for Martian infrastructure.
Since communication lags will limit and delay human intervention, the intricacy of these operations necessitates previously unheard-of levels of autonomy and dependability. Social cohesiveness will depend on the creation of strong communication networks to preserve ties to Earth and cultivate a distinct Martian identity. It will be just as important to comprehend and anticipate psychological stressors through proactive design and support systems as it will be to engineer the physical habitat.
Implications for Psychology and Sociology

Psychological risks from confinement, isolation, and sensory deprivation are just as real as those from radiation. Human resiliency will be put to the ultimate test by living underground on Mars. NASA’s analog missions in isolated deserts and underwater environments demonstrate how crucial meaningful work, group dynamics, and mental health are to survival. Habitats that are designed with modular layouts, virtual reality “windows,” and communal areas can help reduce boredom and claustrophobia.
New governance, collaboration, and conflict resolution models will be tested in the Martian colony; the results may be used to address Earth’s own social problems. Furthermore, since the original colonists will probably come from a variety of backgrounds, the psychological framework needs to take cultural diversity and adaptability into account.
Strategic and Economic Risks

Building underground on Mars is a race for economic and geopolitical supremacy as much as survival. The next frontier of wealth, including rare minerals, intellectual property, and even interplanetary data markets, will be controlled by whoever becomes an expert in extraterrestrial construction and resource extraction.
Since off-world colonies and space-based assets may develop into crucial hubs in international power structures, the strategic ramifications go beyond national security. Additionally, by drawing talent and investment and accelerating innovation cycles, the race promotes the growth of new industries. This aspect of the economy is a strong motivator that guarantees continued dedication and quick advancement. In addition to being a scientific undertaking, the underground Martian civilization is a driving force behind a novel economic paradigm that surpasses the constraints of Earth.
The Opposing Opinion: Why Not Hold Off?

Critics contend that the risks are too high or that colonizing Mars is a diversion from solving Earth’s issues. However, complacency is punished by history. Stasis is inevitable if you wait for “perfect” technology or international agreement. The riskiest tactic of all is inaction.
Waiting also misses the opportunity for Mars colonization to spur technological advancement and global collaboration to address Earth’s problems. Using human ingenuity to broaden the scope of possibility, the Martian underground race represents a proactive response to existential threats. Risks exist, but the price of doing nothing is much higher: lost survival chances, geopolitical marginalization, and technological stagnation.
Unexpected Connections: The Future of Earth and Mars

Life on Earth might be completely transformed by the social structures and technologies developed underground on Mars. Autonomous construction, closed-loop water recycling, and microgrids powered by renewable energy can all be implemented in megacities, deserts, and disaster areas. Mars serves as more than just a standby; it is a testing ground for ideas that could aid Earth in overcoming its own growing problems.
A positive feedback loop of advancement will be produced by the exchange of concepts and technologies between Martian and terrestrial applications. By showing that funding one promotes the other, this collaboration dispels the myth that space exploration and Earth stewardship are mutually exclusive. In the end, Mars is a test of human ingenuity and adaptability, with significant ramifications for the future of our planet.
The “Lava Tube City” Model: An Extreme Case Study
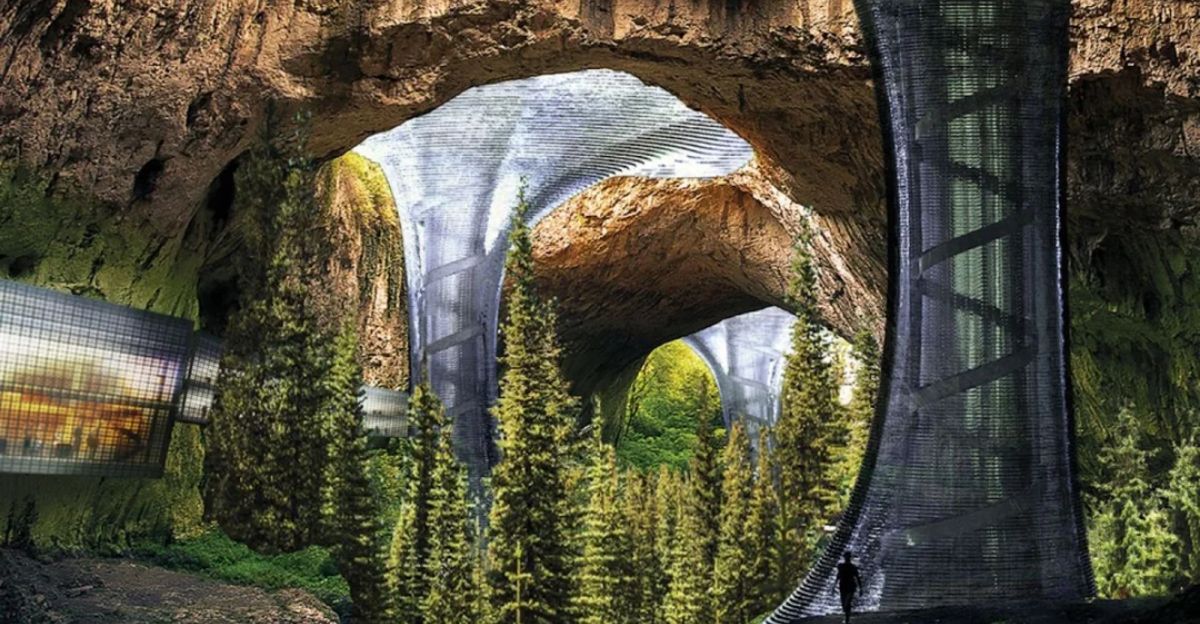

Picture a Martian “Lava Tube City”, kilometers of interconnected, pressurized modules protected by meters of rock, fed by hydroponics and robotic mining, and powered by nuclear and solar microgrids. This model, which is based on NASA’s habitat concepts, permits redundancy and modular expansion; in the event that one section fails, the others are safe. The knowledge gained here would be directly applicable to mining asteroids, lunar bases, or even Earth’s deep-sea habitats.
The potential size and complexity of underground Martian settlements are demonstrated by this extreme case, underscoring the necessity of adaptive management and integrated systems engineering. By placing environmental hazard protection above aesthetics or conventional infrastructure, this model defies accepted urban planning. It is an audacious idea that tests the limits of human creativity and flexibility.
The Intolerant Reasoning of the Martian Race

The race to establish an underground Martian civilization is not a pointless endeavor; rather, it is a strategic imperative for humanity’s long-term survival and well-being. In addition to competing with one another, NASA and SpaceX also have to contend with planetary risk, technological entropy, and the unrelenting passage of time.
This race, which combines practicality with ambitious vision, epitomizes the human spirit of exploration and survival. It recognizes that the future is unpredictable and dangerous, necessitating bravery and fortitude. Humanity’s wager on itself, the underground Martian civilization, is evidence of our ability to overcome obstacles and establish a position among the stars.
Uncover more fascinating moments from history — and hit Follow to keep the stories flowing to your feed!

Don’t miss more incredible stories from the past! Tap Follow at the top of this article to stay updated with the latest historical discoveries. Share your thoughts in the comments — we’d love to hear your perspective!






